Spanish paprika, or pimentón, is a celebrated spice throughout that country, with controlled production that must be monitored to meet traditional standards in how these peppers are grown and processed. Murcia, in southeastern Spain, produces paprika that is sweet and mild. Paprika produced in La Vera, found in western Spain, can be sweet, spicy, or bittersweet. The celebrated pimentón de La Vera are smoked for extra flavor.
Paprika is known for its smoky and slightly bitter flavor, with a spicy kick that ranges from mild to hot. The level of spiciness depends on the type of paprika used, with Hungarian paprika being the spiciest and Spanish paprika being the mildest. The smoky flavor comes from the way the peppers are dried and smoked before being ground into powder. Paprika is commonly used in Hungarian, Spanish, and Moroccan cuisine, and is a key ingredient in dishes such as goulash, paella, and tagines.
The heat of peppers is measured using the Scoville Heat Scale, which ranks the heat of a given pepper in units known as Scoville Heat Units (SHU). Bell peppers of all colors register zero SHU, meaning they're not hot at all. Jalapeños are medium, measuring 2,500 to 8,000 SHU, while extremely hot chiles like habaneros or Scotch bonnets come in at 100,000 to 350,000 SHU.
Polyphenols, such as curcumin, have gained popularity because epidemiological studies have repeatedly shown that diets rich in them can provide inflammatory relief. At the molecular level, polyphenols help stabilize oxidation in cellular components. Oxidation can lead to damage to organelles within cells, including mitochondria, the cell powerhouses where much of the cell's energy is produced by the oxygen we breathe. Eating foods with antioxidant properties, such as berries, nuts, healthy fats, and turmeric, is thought to help maintain levels of oxidative damage.

 They often specialize in specific types of pepper powder, like the famed Sichuan pepper, which offers a unique aroma and mild numbing sensation alongside its heat They often specialize in specific types of pepper powder, like the famed Sichuan pepper, which offers a unique aroma and mild numbing sensation alongside its heat
They often specialize in specific types of pepper powder, like the famed Sichuan pepper, which offers a unique aroma and mild numbing sensation alongside its heat They often specialize in specific types of pepper powder, like the famed Sichuan pepper, which offers a unique aroma and mild numbing sensation alongside its heat
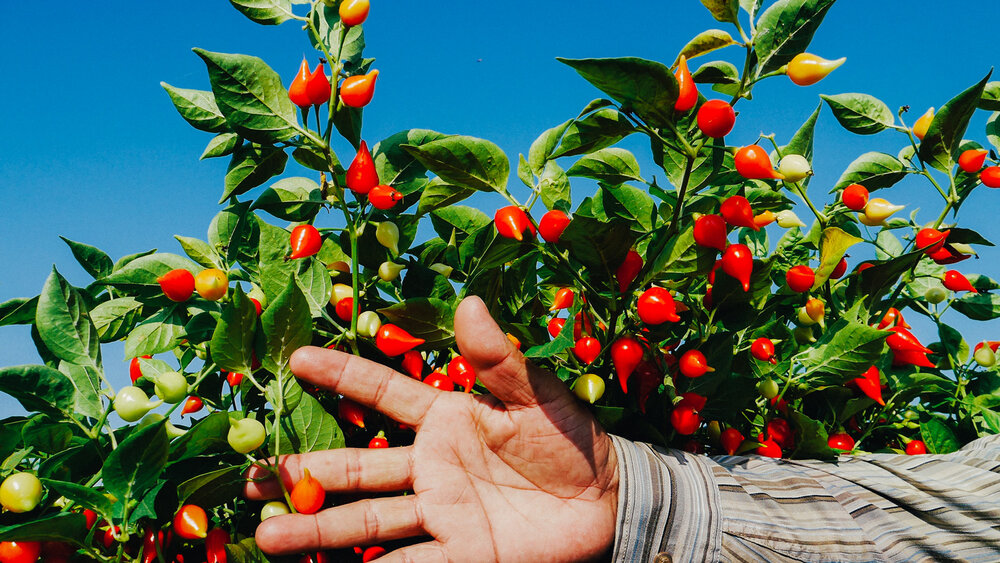 The peppers are then carefully dried under controlled conditions to maintain their flavor and nutritional value The peppers are then carefully dried under controlled conditions to maintain their flavor and nutritional value
The peppers are then carefully dried under controlled conditions to maintain their flavor and nutritional value The peppers are then carefully dried under controlled conditions to maintain their flavor and nutritional value In some cultures, it symbolizes warmth and hospitality, ensuring that guests feel a figurative 'warmth' that mirrors the literal heat of the spice In some cultures, it symbolizes warmth and hospitality, ensuring that guests feel a figurative 'warmth' that mirrors the literal heat of the spice
In some cultures, it symbolizes warmth and hospitality, ensuring that guests feel a figurative 'warmth' that mirrors the literal heat of the spice In some cultures, it symbolizes warmth and hospitality, ensuring that guests feel a figurative 'warmth' that mirrors the literal heat of the spice