Current location:
Links:
-
Another distinguishing factor between these two types of bearings is their internal design and contact angles. Deep groove ball bearings typically have a contact angle of 0 degrees, meaning that they are only designed to accommodate radial loads. In contrast, angular contact bearings have contact angles ranging from 15 to 40 degrees, allowing them to support axial loads efficiently. 22326 bearing plays a crucial role in various industries, including automotive, machinery, and power generation. As a key component in rotating machinery, it is essential to ensure the quality and reliability of the bearing for optimal performance. Design and Functionality In conclusion, a thrust needle roller bearing size chart is an indispensable resource for selecting the appropriate bearing for a particular application. By thoroughly understanding and utilizing this chart, engineers can optimize system performance, minimize maintenance needs, and ensure the longevity of their equipment. Always refer to a reliable and up-to-date chart from a reputable manufacturer to make the best choice for your application. 2. Speed The maximum speed at which the bearing can operate without causing excessive heat generation and wear is known as the maximum operating speed. The maximum operating speed depends on the bearing design, lubrication, and temperature rise.
- Axial Preload: Depending on the specific application, axial preload may be required to optimize the bearing's performance. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for applying the correct axial preload to the bearing. The T7FC045 bearing, a mechanical component often found in various machinery and devices, is a testament to human innovation and engineering prowess. This particular type of bearing, identified by its unique model number, serves as a crucial element in ensuring smooth and efficient operation of systems where rotary or linear motion is involved.
- Noise and Vibration: Thrust ball bearings may generate more noise and vibration compared to other bearing types, particularly under heavy axial loads. This can be a concern in applications where noise and vibration levels must be minimized. One of the key advantages of quantum computing is its ability to solve certain problems much more efficiently than classical methods. For example, M802048 could potentially crack encryption algorithms that are currently considered unbreakable, opening up new possibilities for secure communication and data protection. It could also accelerate the search for new drugs and materials by simulating complex chemical reactions and molecular interactions, potentially leading to more effective treatments and innovative materials It could also accelerate the search for new drugs and materials by simulating complex chemical reactions and molecular interactions, potentially leading to more effective treatments and innovative materials
- Containment of Lubrication: The deep groove in a single row deep groove ball bearing provides space for lubricant, such as grease or oil, which helps to reduce friction, dissipate heat, and protect the bearing from wear and corrosion. Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of the bearing. The choice of material is crucial for the performance of high temperature bearings. Chrome steel is a popular choice due to its good combination of strength, hardness, and toughness. Stainless steel is also commonly used because it has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures up to 120°C Stainless steel is also commonly used because it has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures up to 120°C
One of the key features of ball thrust bearings is their ability to support axial loads in a specific direction. This makes them ideal for applications where heavy loads need to be transmitted in a straight line, such as in gearboxes, automotive transmissions, and machine tool spindles. By utilizing the rolling action of the balls, ball thrust bearings can handle much higher loads than plain bearings or sleeve bearings.
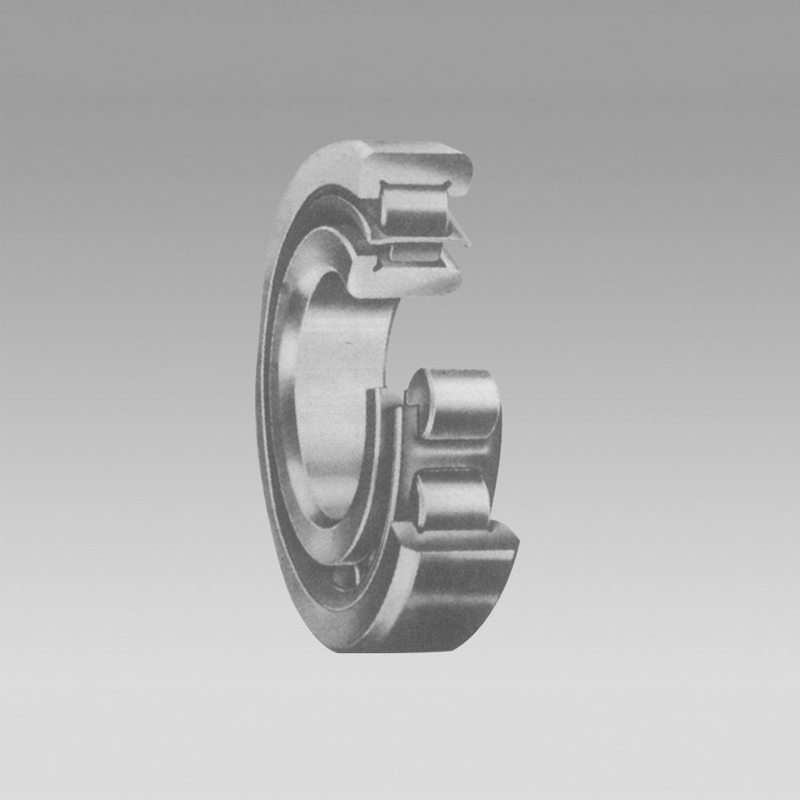
Taper roller bearings are a type of rolling element bearing that is designed to withstand heavy loads and provide efficient rotation. These bearings consist of an inner ring with a conical raceway, an outer ring with a matching conical raceway, and a row of tapered rollers that are contained between the two raceways. The unique design of these bearings allows them to support both radial and axial loads, making them ideal for use in a wide range of applications. Introduction In conclusion, the Bearing 6301 AS 15 is more than just a standard part; it is a testament to the marriage of precision engineering and practicality. Its role in ensuring the smooth running of countless machines and systems underscores its significance in modern technology. As we continue to rely heavily on mechanical systems, the role of bearings like the 6301 AS 15 becomes increasingly vital, making them an integral part of our everyday lives, often operating quietly in the background, but playing a crucial role in our industrial landscape. In conclusion, single deep groove ball bearings are a reliable and efficient solution for various industrial applications. Their high-speed capabilities, low friction, and versatility make them a popular choice for machinery and equipment manufacturers. With proper maintenance and care, these bearings can provide long-lasting and trouble-free operation in a wide range of operating conditions. Whether in a factory setting or a consumer product, single deep groove ball bearings play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and reliable performance. Understanding the Specifications of the 6303 Bearing
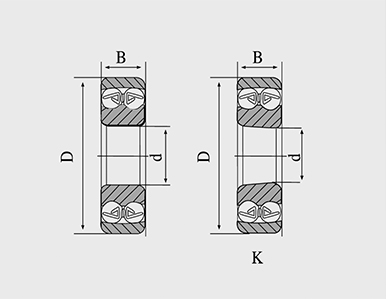
A deep groove in a ball bearing refers to the specific design feature of the bearing's inner and outer raceways, which allows it to accommodate radial and axial loads while enabling smooth and efficient rotation. The deep groove is a critical aspect of the ball bearing's construction and contributes to its performance in various applications.
Double row spherical roller bearings, a pinnacle of engineering excellence, are an integral part of various industrial applications where high load capacity and durability are paramount. At the forefront of this technology is SKF, a global leader in bearing manufacturing, known for its commitment to precision and reliability. When it comes to installation, it's important to ensure that the bearing is properly aligned and seated in its housing2. Brand Different bearing manufacturers may have varying production costs, branding strategies, and marketing expenses, which can all affect the final price of their products. Well-known brands often command a premium price due to their reputation for reliability and performance. Bearing 32211 is commonly used in a variety of applications, including When discussing thrust bearings by size, it's crucial to understand that size isn't just about aesthetics; it directly impacts performance and application suitability. Thrust bearings come in various sizes, ranging from miniature to large-scale, each tailored to specific industrial requirements. Miniature thrust bearings, for instance, find extensive use in compact devices like cameras or watches, where space is limited yet precise movement is demanded. Their small size allows them to fit into tight spaces while providing reliable support. The secret behind the 6004 ball bearing's superiority lies in its meticulous design and construction. Made up of a series of precision-crafted components, including an inner ring, outer ring, and a cage that holds the balls in place, this bearing is engineered to maintain its shape and alignment under the most demanding conditions.
* Automotive components, such as axles and transmissions where * C is the radial clearance An In-depth Look at Thrust Bearings by Size When comparing durability, cylindrical roller bearings generally have a higher capacity for load carrying due to the larger contact patch between the roller and races 2. Renewable energy The bearing's durability and efficiency make it ideal for use in wind turbines and other renewable energy systems, where reliability and performance are critical. In the realm of mechanical engineering, bearings play an essential role in reducing friction and supporting loads in rotating or linear motion systems. Among the various types of bearings, the full complement cylindrical roller bearing stands out for its unique design and performance capabilities. This article delves into the intricacies of this specialized bearing, exploring its construction, advantages, and applications. Maintenance of the 24128 bearing is relatively straightforward but crucial for optimal performance. Regular inspections to check for signs of wear or damage should be conducted. Lubrication must be maintained at the recommended levels to prevent premature degradation. If properly cared for, these bearings can significantly outlast their expected service life, offering excellent value for the investment made in high-quality machinery components. 1. Gearboxes These bearings are commonly used in gearboxes to support heavy loads and reduce friction between moving parts. When selecting the right deep groove ball bearing for your application, it's essential to consider several factors, including the bore size, outer diameter, width, and cage type. This article provides a comprehensive size chart guide to help you make an informed decision. In conclusion, while Ball Bearings offer simplicity and efficiency in handling radial loads, Deep Groove Ball Bearings expand the scope with their additional axial load-bearing capability and versatility. Each type has its niche, and selecting the right one depends on factors such as load requirements, speed, alignment tolerance, and operational environment. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimal machine performance and longevity.
 It could also accelerate the search for new drugs and materials by simulating complex chemical reactions and molecular interactions, potentially leading to more effective treatments and innovative materials It could also accelerate the search for new drugs and materials by simulating complex chemical reactions and molecular interactions, potentially leading to more effective treatments and innovative materials
It could also accelerate the search for new drugs and materials by simulating complex chemical reactions and molecular interactions, potentially leading to more effective treatments and innovative materials It could also accelerate the search for new drugs and materials by simulating complex chemical reactions and molecular interactions, potentially leading to more effective treatments and innovative materials m802048. The Significance of the NU 209 Bearing in Modern Engineering The primary advantage of deep groove ball bearings is their ability to accommodate both radial and axial loads simultaneously. This makes them suitable for use in a wide variety of applications, including conveyor systems, pumps, fans, turbines, and more. The bearings' ability to distribute loads evenly helps to reduce wear and tear, resulting in less frequent maintenance and downtime. In conclusion, the AN2002 series single-row deep-groove ball bearing is an excellent choice for applications that require high rotational speeds, heavy loads, and resistance to misalignment. With their superior performance, durability, and versatility, these bearings are sure to provide reliable service in a wide range of industrial environments.
m802048. The Significance of the NU 209 Bearing in Modern Engineering The primary advantage of deep groove ball bearings is their ability to accommodate both radial and axial loads simultaneously. This makes them suitable for use in a wide variety of applications, including conveyor systems, pumps, fans, turbines, and more. The bearings' ability to distribute loads evenly helps to reduce wear and tear, resulting in less frequent maintenance and downtime. In conclusion, the AN2002 series single-row deep-groove ball bearing is an excellent choice for applications that require high rotational speeds, heavy loads, and resistance to misalignment. With their superior performance, durability, and versatility, these bearings are sure to provide reliable service in a wide range of industrial environments.  Stainless steel is also commonly used because it has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures up to 120°C Stainless steel is also commonly used because it has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures up to 120°C
Stainless steel is also commonly used because it has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures up to 120°C Stainless steel is also commonly used because it has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures up to 120°C high temperature deep groove ball bearing. 2
high temperature deep groove ball bearing. 2 an 02-series single-row deep-groove ball bearing is to be selected. High Speed Capability These bearings are designed to operate at high speeds, making them ideal for use in high-speed rotating machinery such as pumps, fans, and turbines. Cylindrical roller bearings, an essential component in various mechanical and engineering applications, play a crucial role in facilitating smooth and efficient rotation while supporting heavy loads. These bearings, with their unique design featuring cylindrical rollers, offer high radial load capacity and excellent rigidity, making them indispensable in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. Thirdly, the market demand for 6307 bearings can influence their price
an 02-series single-row deep-groove ball bearing is to be selected. High Speed Capability These bearings are designed to operate at high speeds, making them ideal for use in high-speed rotating machinery such as pumps, fans, and turbines. Cylindrical roller bearings, an essential component in various mechanical and engineering applications, play a crucial role in facilitating smooth and efficient rotation while supporting heavy loads. These bearings, with their unique design featuring cylindrical rollers, offer high radial load capacity and excellent rigidity, making them indispensable in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. Thirdly, the market demand for 6307 bearings can influence their price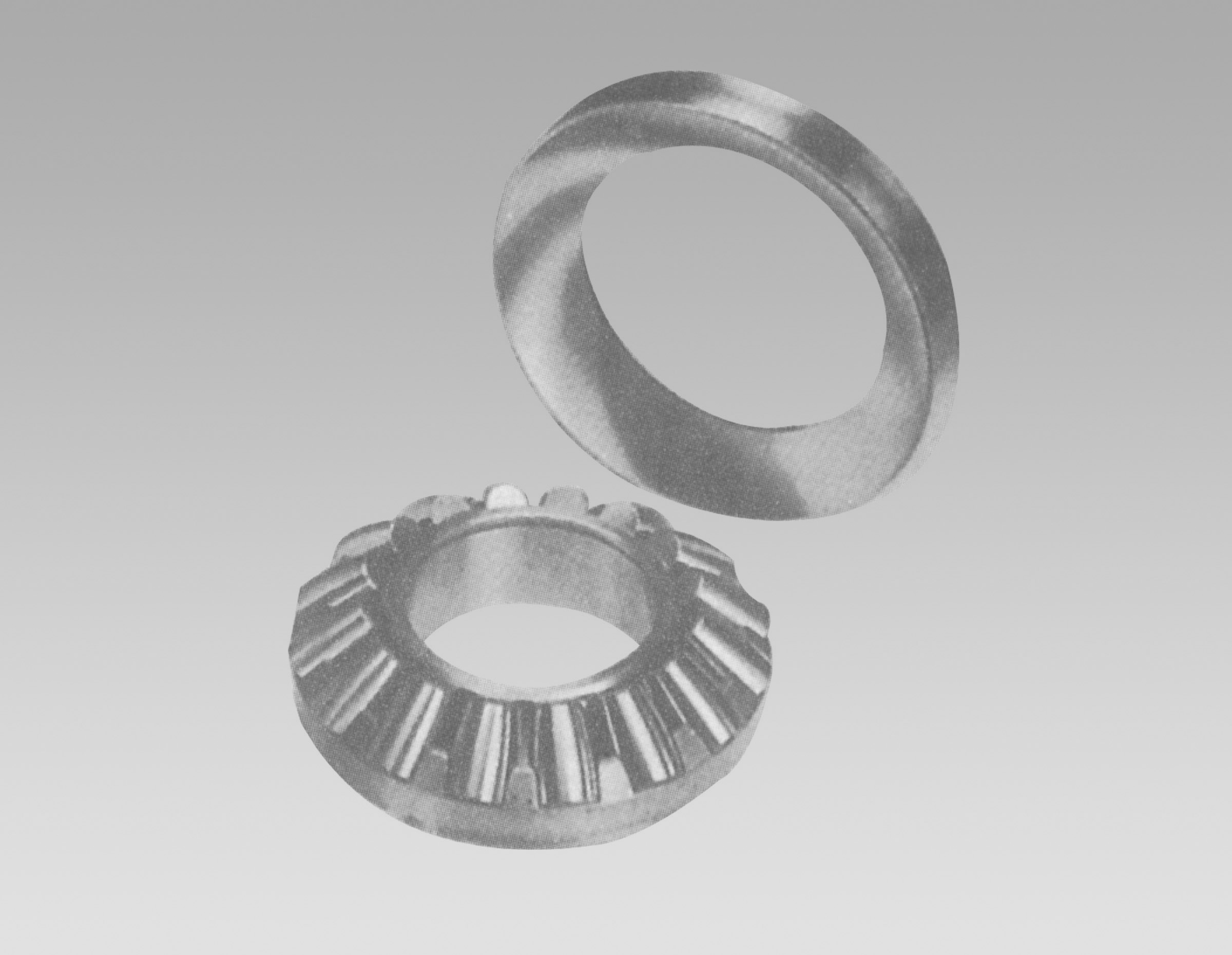 6307 bearing price. If there is high demand for these bearings, suppliers may increase their prices to capitalize on the market trend. On the other hand, if there is low demand, suppliers may reduce their prices to attract buyers and move inventory. The material composition of the NU 316 bearing is another factor contributing to its durability and resilience
6307 bearing price. If there is high demand for these bearings, suppliers may increase their prices to capitalize on the market trend. On the other hand, if there is low demand, suppliers may reduce their prices to attract buyers and move inventory. The material composition of the NU 316 bearing is another factor contributing to its durability and resilience